Diagnosis of leishmaniasis

The mainstay of diagnosis of canine leishmaniasis is based on several premises: Detection of the parasite by cytology or histopathology of lesions. Serology and proteinogram. Additional tests: PCR, bone marrow cytology, etc. Serology should always be accompanied by a proteinogram, as it can provide valuable information on the active state of the disease. Bone […]
Basic spirometry interpretation
Spirometry is the measurement of gas flow and volume during respiration. Many of the current systems also allow the measurement of airway pressures, which provides a series of respiratory curves and loops that are very useful for the detection of respiratory complications. In this video we will review the information provided by these curves and […]
Spinal trauma
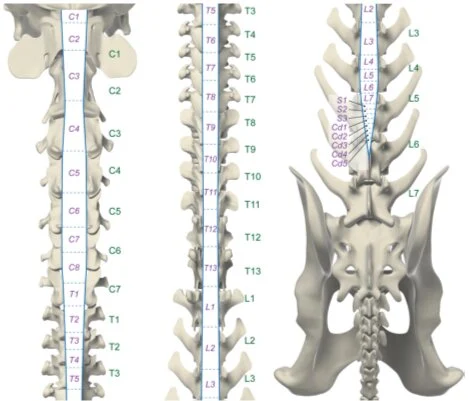
The severity and extent of the spinal cord injury determine the appearance of particular clinical situations with characteristic signs such as: Schiff-Sherrington posture: the patient is in lateral decubitus, with extensor hypertonia of thoracic limbs (maintaining voluntary motor function), hypotonia of pelvic limbs with normoreflexia (intact spinal reflexes) and tendency to opisthotonos. Spinal shock: loss […]
Systemic Ischaemia-Reperfusion Syndrome

Definition: Sepsis-like clinical presentation as patients present with systemic inflammation (SIRS), coagulation activation (DIC) and endothelial disruption. Clinical signs: tachycardia/bradycardia tachypnoea fever/hypothermia hypoperfusion multi-organ failure bleeding, oedema, etc. Treatment: Haemodynamic optimisation: use of early goal-directed therapy. Our goals will be a central venous pressure of 0-10 cm H2O, MAP 80-120 mmHg, ScvO2 > 70% and […]
Clinical signs in feline hypertension
The clinical signs that can be observed are based on the lesions caused in the target organs: In the eyes: retinopathies (from retinal detachments to papillary oedema, or bullous retinopathies, ingurgitation of retinal vessels to sudden blindness with severe mydriasis). We can also observe haemorrhages in both retina and anterior chamber hyphema. In the kidneys: […]
Oral examination and diagnosis in dogs and cats
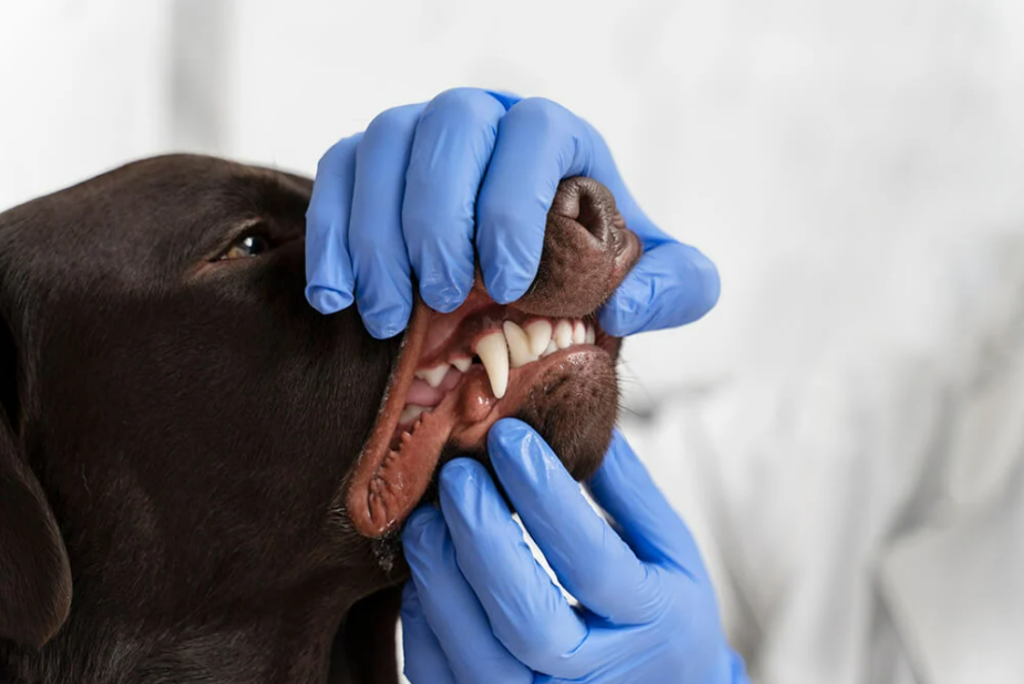
The examination of the head and mouth of our patients is a fundamental part of their physical examination. In order to be able to make a proper diagnosis and, therefore, propose a treatment, it is important to systematise our examination. The examination of the patient will consist of two distinct episodes: Clinical examination, whenever and […]
Would you know how to treat grape poisoning?

Grapes and sultanas are fruits of the genus Vitis spp. They cause acute renal failure in dogs due to proximal tubular necrosis. Treatment will depend on the time of ingestion and the development of renal failure. If it is a recent ingestion without renal damage, it is recommended to induce emesis, administer repeated doses of […]
Anaesthetic Maxillary Nerve Block In The Dog
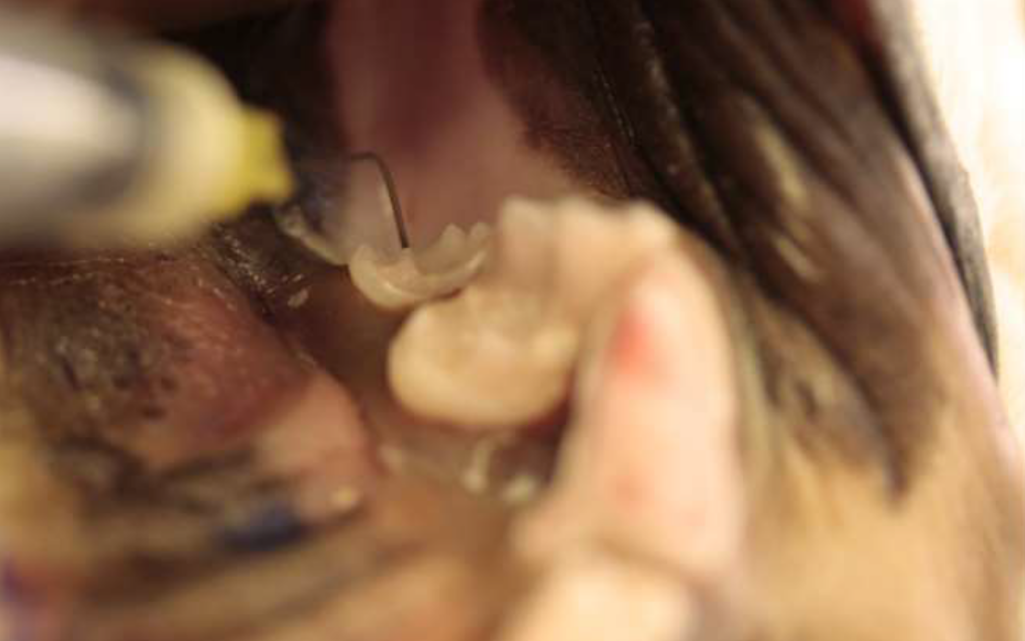
Any surgical procedure in the mouth of our patients is painful. It is our duty as veterinarians to use all the resources that modern medicine provides to avoid pain and suffering. Anaesthetic blocks are regional anaesthetic techniques that prevent the propagation of the afferent nociceptive stimulus from the peripheral nerves to the central nervous system, […]
Diabetic cats, which Insulin do you prefer for their treatment?

Insulins for the treatment and stabilisation of glycaemia in feline medicine have evolved a lot in the last 20 to 25 years. We have gone from using preparations that were not always sufficiently effective or even dangerous to insulins that we can call «modern» and that allow the owner to administer these hormonal drugs without […]
Management of Hyperkalemia

When should hyperkalemia be treated? It is usually from levels above 6.5 mEq/L. Above 7.5 mEq/L treatment should be more aggressive. ¿Qué fármacos usamos para tratarla? Drug Dose Mechanism of action Comments Calcium gluconate 10% 0.5 – 1.5 ml/kg slow IV with ECG It reduces cardiac excitability by restoring the gradient between resting potential […]


